The next topic of Microbiology is topic 2 – Microscopy
Techniques. The learning outcomes for this topic are:
a)
To
identify the parts of a basic microscope (C3)
| Parts of a microscope |
b)
To
describe the principle of light, phase-contrast, fluorescence and electron microscope (C2)
| Image from electron micoscope |
c)
To
select suitable microscope for relevant usage (P1)
| Lab microscope that I have used before |
d)
To
recognize images produced form different microscope (A2)
\
\
From the learning outcomes listed above, it seems like I have
to memorize a lot of things such as the parts of the microscope and its
function. Other than that, I also have to know types of different microscope
used to detect presence of microbes.
As we all know, we all have to choose an adopted microbe and do an intense research on it and will present our findings later on a three minute talk. So, Dr Wan asked us to put up our microbe’s name on padlet. The microbe that I choose to adopt is Vibrio haemolyticus. Vibrio haemolyticus is a type of bacteria that has a vibrio shape based on its name. Vibrio shape is like a ‘coma’ or curved rods shape. Vibrio haemolyticus is a Gram-negative bacterium found in brackish saltwater, which, when ingested causes gastrointestinal illness in humans. So basically this is a pathogenic bacteria. I chose this bacterium because I found it is interesting and I am enthusiast to know more about this microbe.
As we all know, we all have to choose an adopted microbe and do an intense research on it and will present our findings later on a three minute talk. So, Dr Wan asked us to put up our microbe’s name on padlet. The microbe that I choose to adopt is Vibrio haemolyticus. Vibrio haemolyticus is a type of bacteria that has a vibrio shape based on its name. Vibrio shape is like a ‘coma’ or curved rods shape. Vibrio haemolyticus is a Gram-negative bacterium found in brackish saltwater, which, when ingested causes gastrointestinal illness in humans. So basically this is a pathogenic bacteria. I chose this bacterium because I found it is interesting and I am enthusiast to know more about this microbe.
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus na TCBS agaru |
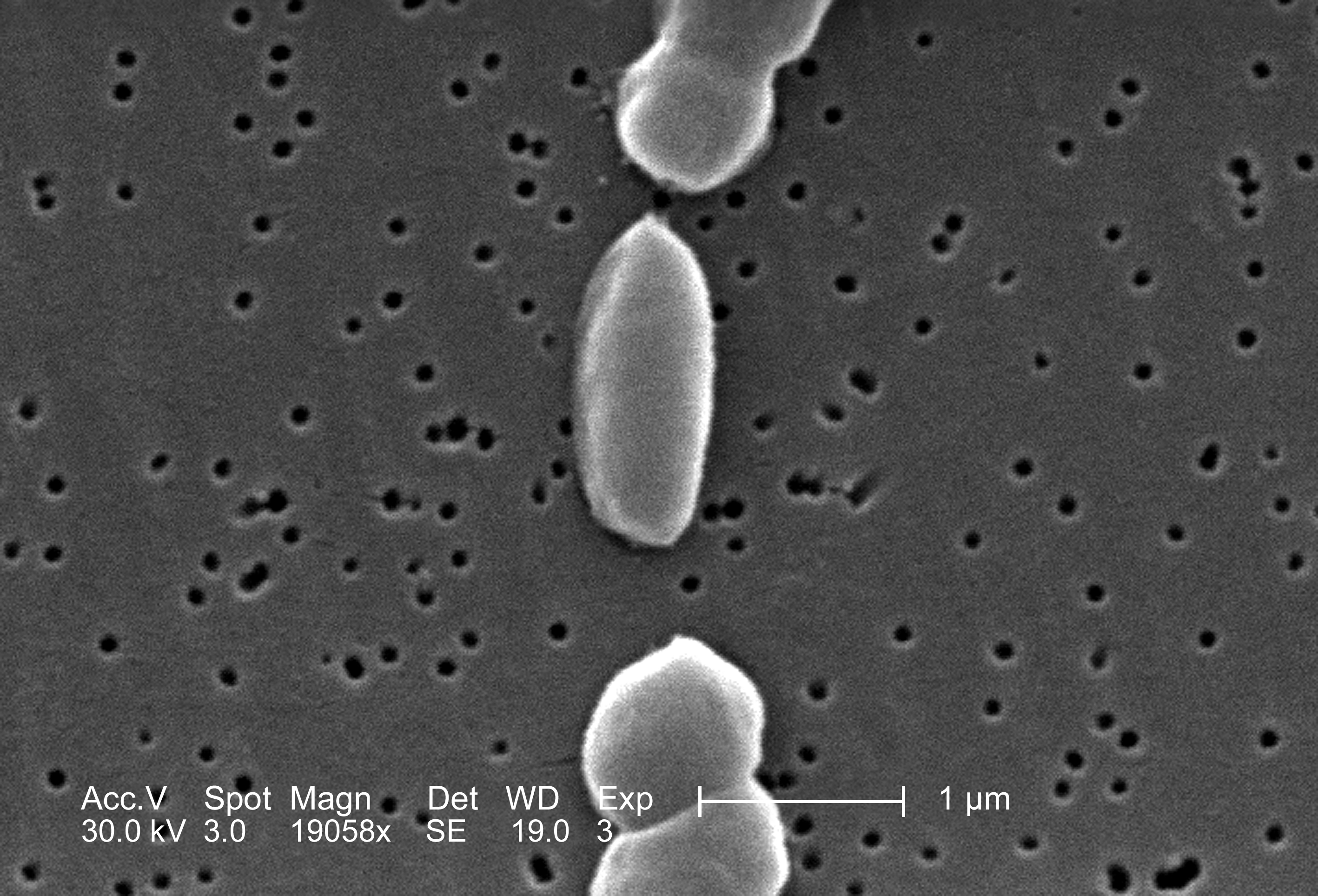 |
| Vibrio haemolyticus |
Before we went to the next class, Dr Wan asked us to look for a few terms. They are ‘pleomorphic’, ‘mycoplasma’. ‘thermoplasma’ and ‘vampyrellid’. Honestly, I have never heard any of these terms, thus, I really have to look for the definition of these terms on the internet or in a textbook. The outcome of my findings are; pleomorphic means an ability of some bacteria to alter their shape or size in response to environmental conditions. These environmental conditions usually are not favourable to the microbes, thus, the microbe will have this ability to encounter unusual conditions. Pleomorphism has been observed in some members of Deinococcacae family. They can change shape or size because they lack of cell wall or they have no cell wall. The second term is mycoplasma. Mycoplasma is a genus of bacteria that lack a cell wall around their cell membrane. Without a cell wall, they are unaffected by many common antibiotics such as penicillin that target cell wall synthesis. Most surprising fact about mycoplasma is that mycoplasma is the SMALLEST MICROBE IN THE WORLD! It’s amazing right?! This is the perks of studying microbiology, you get shocked on every facts that you just heard. Haha. :)
| Mycobacterium |
Thermoplasma on the other hand is an archae which can thrive
in acidic and high-temperature environments . Thermoplasma is a microbial
biorealm page on the genus Thermoplasmataceae (Thermoplasma acidophilum). Thermoplasma
are facultative anaerobes and respire using sulfur and organic carbon. They do
not contain a cell wall but instead contain a unique membrane composed mainly of a tetraether lipoglycan
containing atypial archaeal tetraether lipid attached to a glucose and mannose
containing oligosaccharide. This lipoglycan is presumably responsible for the
acid and thermal stability of the Thermoplasma
membrane. Vampyrellid are a group
cercozoans with filose pseudopods and lacking shells. Vampyrella is typical of
the group, which also contains such as Platyreta and Arachnula. The term
“Aconchulinida” is sometimes used for vampyrellid.
 |
| Cultured E.coli O157:H7 |
New information that I get from this class is about E.coli. Escherichia coli (abbreviated as E.coli) are bacteria found in the environment, foods and lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. But there are several names for E.coli such as E.coli 0157:H7. The difference in the names is because of the strains of E.coli bacteria. E.coli 0157:H7 can cause severe anemia or kidney failure, which can lead to death. Escherichia coli 0157:H7 is an enterohaemorrhagic serotype of the bacteria E.coli and a cause of illness, typically through consumption of contaminated and raw food including raw milk. Infection with this type of pathogenic bacteria may lead to haemorrhagic diarrhea and to kidney failure.
There’s something unique happened on this week which was Dr
Wan asked Radin’s group to figure out how to learn about the parts of the
microscope. They must be able to make us understand and have fun while learning
it. When Radin’s group present their slides, it is not about the parts of a
microscope but rather about how the first microbes was observed under the first
microscope.
So basically, it is not what was Dr Wan wanted but I must compliment what they did were weird, funny and interesting. I like their presentation. We all were laughing because in between their slides they put funny photos and jokes inside the slides. We had a fun time for a moment.
| Early microscope |
So basically, it is not what was Dr Wan wanted but I must compliment what they did were weird, funny and interesting. I like their presentation. We all were laughing because in between their slides they put funny photos and jokes inside the slides. We had a fun time for a moment.
And we also play a quiz on Kahoot.it. This is the first time
I heard about Kahoot.it. Very interesting and energetic quiz. We have only 10
seconds for every questions of the quiz and if we answer it correctly, our
names will be displayed on the projector screen. I am looking forward to play
Kahoot.it again. But maybe that day is not my lucky day, I did not manage to get my name displayed on the
screen.
 |
| Kahoot.it |
Topic 2 really surprised me in every possible way. I learned
a lot about microscope. There are 4 types of microscope which are optical
microscope, electron microscope, scanning probe microscope and scanning
acoustic microscope.
| Optical microscope |
The optical microscope can be divided into dark field, bright
field, fluorescence microscopy and phase contrast microscopy. These optical
microscope or light microscope are
compound microscope. The bright-field microscope produce dark image against
brighter background. Bright-field microscope used to enhance observation with
bright-field microscope, kill and stain the cells. Meanwhile the dark-field microscope produce
bright image against darker background. Dark-field microscope usually used to
observe live specimens which cannot be stained. Phase contrast microscopy light
coming in is in phase and when it strikes the image is it thrown out of phase
creating more resolution. Phase contrast microscope also enhances contrasts of
transparent and colourless objects by influencing the optical path of light.
Fluorescence microscope produces image from light that passes through a
specimen. Specimen tagged or naturally fluorescing against dark background. The
specimen are exposed to uv, violet or blue light.
Electron microscopy can be divided into 2 that are
transmission electron microscope to analyse internal structures and scanning
electron microscope to analyse surface structures.

Atomic force (scanning probe) microscopy uses electrons and
application of small voltage to the specimen. It allows observation and
manipulation at molecular and atomic level.
Scanning acoustic microscopy used sound waves and usually for
studying larger specimens like bacterial biofilms and cancer cells.
There are different types of stains for specimens. There are
simple stains, differential stains, acid fast stains and special stains. Simple
stain is a very simple staining procedure involving only ONE stain. Basic stain
such as methylene blue, Gram safranin/ Gram crystal violet are useful for
staining most bacteria.
Differential staining is used to stain physical and chemical properties of different groups of bacteria. It allows us to differentiate between different kinds or parts of bacterial cell.
Acid fast stain or ‘Ziehl-Neelson stain’ is a differential stain used to identify acid-fast organisms such as members of the genus mycobacterium. Acid-fast organisms are characterized by wax-like, nearly impermeable cell wall; they contain mycolic acid and large amounts of fatty acid , waxes and complex lipids. Usually Ziehl-Neelsen stain used to stain bacteria that is very fussy called fastidious microbes (high fatty acid).
Special stains will stain certain structure such as flagella, capsule and endospore. Colostrodium and bacillus (Bacillus anthracis) are types of bacteria that used endospores.
| Simple stain |
| Differential staining |
Differential staining is used to stain physical and chemical properties of different groups of bacteria. It allows us to differentiate between different kinds or parts of bacterial cell.
Acid-fast staining |
Acid fast stain or ‘Ziehl-Neelson stain’ is a differential stain used to identify acid-fast organisms such as members of the genus mycobacterium. Acid-fast organisms are characterized by wax-like, nearly impermeable cell wall; they contain mycolic acid and large amounts of fatty acid , waxes and complex lipids. Usually Ziehl-Neelsen stain used to stain bacteria that is very fussy called fastidious microbes (high fatty acid).
Special stains will stain certain structure such as flagella, capsule and endospore. Colostrodium and bacillus (Bacillus anthracis) are types of bacteria that used endospores.
For the next topic, Prokaryotes, Dr Wan asked us to make a
mindmap of prokaryote and submit it to Putrablast. Doing a mindmap before going
to class helped me to be ready about what to learn next. I have done my mindmap
using Popplet.com. I managed to get as many information as possible and put it
into my mindmap. I am satisfied with my mindmap. Truly, by doing a mindmap has
helped me understand a certain topic better. I will try to do a mindmap for
every topic if possible.
 |
| Mindmap |
Overall, it can be seen that I learned a lot about topic 2
Microscopy Technique. The techniques are all very high technology and very
useful for us to see small microbes. We should be thankful to the inventors of
various microscope because they help us to learn microbiology easier.
No comments:
Post a Comment